Squamous Cell Cancer: It’s Pictures, Symptoms, Treatment, and More
Table of content
Squamous cell cancer (SCC), additionally regarded as squamous cell carcinoma, is a kind of cancer. It develops in squamous cells, which are the thin, flat cells that make up the outermost layer of your skin. Squamous cells are additionally discovered in different components of your physique such as your lungs, mucous membranes, digestive tract, and urinary tract.
SCC that types in your pores and skin is recognised as cutaneous SCC (cSCC). cSCC develops due to modifications in the DNA of squamous cells, which motives them to multiply uncontrollably. It regularly types on components of your pores and skin regularly uncovered to daylight like your face, neck, or arms.
Keep studying to study extra about this kind of pores and skin cancer, what it appears like, what reasons it, and how it’s recognized and treated.
ALL ABOUT CANCER >>
What is squamous cellphone pores and skin cancer?
Cutaneous SCC (cSCC) is a most cancers that develops in the squamous cells of your skin. According to the Skin Cancer Foundation, about 1.8 million people in the United States are identified with cSCC every year. It’s the second most common type of pores and skin cancer.
Although cSCC isn’t lifestyles threatening, it can grow to be risky if it goes untreated. When cure isn’t acquired quickly, the growths can enlarge in measurement and unfold to different components of your body, inflicting serious complications.
People with cSCC regularly enhance scaly, purple patches, open sores, or warty growths on their skin. These extraordinary growths can improve anywhere, however they’re most frequently located in areas that get hold of the most publicity to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, both from daylight or from tanning beds or lamps.
Oral SCC additionally makes up greater than 90 percent of mouth cancers. Lung SCC makes up about 30 percentage of a team of lung cancers called non-small cellphone lung cancer and about 25 percentage of lung cancers overall.
IMPORTANCE OF MEDICAL BILLING AND CODING >>
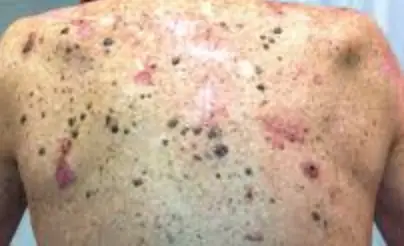
What does squamous cellphone carcinoma seem like?
Here are some examples of what squamous cellphone carcinoma can appear like:
Types of pores and skin cancer
Your skin has a couple of layers. The outer, defensive layer of the pores and skin is acknowledged as the epidermis. The dermis has three foremost sorts of cells:
- Keratinocytes (skin cells, additionally known as squamous cells)
- Melanocytes (pigment-producing cells)
- Langerhans cells (immune cells)
The cells of the dermis are continuously shedding to make way for fresh, new pores and skin cells.
However, when positive genetic adjustments manifest in the DNA of any of these cells, pores and skin most cancers can occur. The most important kinds of pores and skin most cancers are:
- Squamous phone carcinoma
- Basal mobile carcinoma
- Malignant melanoma
- Squamous cellphone cancer
Squamous cells are the cells closest to your skin’s surface, and their reason is to line your skin. cSCC regularly develops in areas of the physique that are regularly uncovered to UV radiation, such as your face, hands, and ears.
MESOTHELIOMA AND LUNG CANCER >>
Basal mobile cancer
Basal cells take a seat beneath the squamous cells, and they’re continuously dividing to structure new cells. According to the American Cancer Society, basal cellphone carcinoma makes up about 80 percentage of pores and skin cancers.
Like cSCC, basal cellphone most cancers usually develops in areas uncovered to UV rays, in particular your face and neck. This kind of most cancers tends to develop slowly, and it not often spreads to different components of your body.
However, if basal telephone most cancers goes untreated, it can in the end unfold to your bones and different tissues.
MORE ON SQUAMOUS CELL CANCER >>
Melanoma
Along with basal cells, melanocytes are placed in the deepest area of your epidermis. These cells are accountable for producing melanin, the pigment that offers pores and skin its color. When most cancers develops in melanocytes, the circumstance is regarded as malignant melanoma.
Malignant melanoma is much less frequent than squamous telephone and basal cancers, however it’s extra possibly to develop and unfold when it’s left untreated.
What are the signs and symptoms of squamous cellphone cancer?
cSCC frequently happens in areas uncovered to UV radiation, such as your face, ears, and hands. However, it can additionally show up in your mouth, round your anus, and on your genitals.
ALCOHOL AND DRUG DETOX AND CENTERS >>
Symptoms of cSCC can include:
- An open sore that can have raised borders
- A scaly, reddish patch of skin
- A brown spot equivalent to an age spot
- A wart-like growth
- New increase on an historical scar, birthmark, or mole
- A horn-shaped growth
- A association and dome-shaped growth
According to the American Academy of Dermatology, cSCC is most normally purple or pink. It can additionally be:
- Brown
- Black
- Yellowish
- White
In your mouth, this most cancers can cause:
- Lip or mouth sores that don’t heal
- Sore or hard patches in your mouth
- A loose tooth
- White or reddish patches
- Painful swallowing
- A boom inner your mouth
It’s a correct thought to make an appointment with your medical doctor or dermatologist proper away if you note any signs of cSCC or trip a sore or increase that doesn’t heal. An early analysis and remedy are vital for stopping complications.
BEST EXERCISE AND WORKOUT FOR CANCER >>
What are the motives and chance elements for squamous Cell cancer?
cSCC is prompted with the aid of mutations that show up in squamous cellphone DNA. These adjustments motive unusual cells to multiply out of control.
UV radiation is the most frequent motive of the DNA mutations that lead to cSCC and different skin cancers.
ALL ABOUT PERITONEAL MESOTHELIOMA >>
Causes of squamous cell cancer
Most instances of cSCC are attributed to publicity to UV radiation from daylight or indoor tanning gear like tanning lamps and beds. Other practicable reasons include:
Genetics: Genetic factors seem to play a function in the improvement of cSCC. A 2015 find out about observed that humans with a household records of cSCC are about four instances extra possibly to enhance it.
Smoking: People who smoke are more in all likelihood to increase cSCC, specially on their lips. Smoking is the predominant danger aspect for creating lung cSCC and different non-small telephone lung cancers.
Chemical exposure: Exposure to sure chemical compounds such as coal tar, paraffin, some petroleum products, and arsenic can also make contributions to cSCC development.
Radiation exposure: Undergoing radiation therapy slightly will increase your danger of growing pores and skin most cancers in the phase of your physique that acquired treatment.
Immunosuppression: Immunosuppression contributes to the improvement of cSCC. For example, organ transplant recipients have a 65 to 250 instances greater danger of creating cSCC than human beings in the frequent population.
Severe burn scars and sores: cSCC can advance in extreme burn scars, sores, or ulcers that have been on your physique for many years.
Risk elements for squamous mobilephone cancer
Risk elements for cSCC include:
- Having honest skin
- Having light-colored hair and blue, green, or grey eyes
- Having long-term publicity to UV radiation
- Living in sunny areas or at a excessive altitude
- Having a records of more than one extreme sunburns, mainly if they passed off early in life
- Having a records of being uncovered to chemicals, such as arsenic
- Having a records of immunosuppression
- History of severe burn scars, ulcers, or sores
DIAGNOSING MESOTHELIOMA >>
How is squamous telephone most cancers treated?
Treatment for cSCC varies. Treatment is primarily based on:
- The extent and severity of your cancer
- Your age
- Your average health
- The region of the cancer
If cSCC is caught early, the circumstance can generally be efficiently treated. It turns into more difficult to therapy as soon as it has spread. Many redress can be carried out as in-office procedures. Treatments might also include:
Mohs micrographic surgery: In Mohs surgery, your health practitioner makes use of a scalpel to cast off the extraordinary pores and skin and some of the surrounding tissue. The pattern is right away examined underneath a microscope. If there are any most cancers cells in the sample, the method is repeated till no most cancers cells are found.
Excisional surgery: During excisional surgery, your health practitioner eliminates the most cancers cells as nicely as a skinny layer of wholesome pores and skin in the surrounding area. Stitches are used to shut the wound. The pattern is then despatched to a laboratory to make sure the complete cancerous region has been removed.
Electrosurgery: Also known as electrodesiccation and curettage, electrosurgery involves scraping off the most cancers and burning the pores and skin to kill most cancers cells. This technique is normally executed greater than as soon as to make certain thorough cure and whole elimination of the cancer.
Cryosurgery: During cryosurgery, your health practitioner makes use of liquid nitrogen to freeze and damage the cancerous tissue. Like electrosurgery, this therapy is repeated more than one instances to make positive all cancerous tissue has been eliminated.
Radiation: With radiation, excessive strength X-rays kill most cancers cells. This cure is administered externally by using a machine, which ambitions the rays at the affected area. Radiation is frequently performed a couple of instances a week for a number of weeks.
Photodynamic therapy: Also regarded as PDT, photodynamic therapy involves the software of a photosensitizing substance to the cancerous areas. After 1 to three hours or longer, the areas that had been medicated are uncovered to sturdy mild for various minutes. This prompts the remedy that used to be utilized and kills peculiar cells.
Systemic drugs: Several kinds of systemic tablets are FDA permitted to deal with cSCC, along with cemiplimab-rwlc (Libtayo) and pembrolizumab (Keytruda). Systemic tablets act on your entire physique and are frequently used for aggressive cSCC.
Non-FDA-approved strategies for treating squamous phone carcinoma
Some docs might also additionally use laser surgical treatment and topical medicinal drugs to deal with cSCC. However, the Food and Drug Administration has now not authorised these strategies for treating cSCC:
Laser surgery: During laser surgery, your physician makes use of a targeted beam of mild to eliminate areas of pores and skin that are abnormal.
Topical medications. Medications, such as 5-fluorouracil and imiquimod, that are utilized on the pores and skin to deal with different pores and skin cancers may additionally additionally assist deal with cSCC.
Once cSCC has been treated, it’s necessary to attend all follow-up visits with your doctor. cSCC can return, and it’s necessary to reveal your pores and skin for any precancerous or cancerous areas at least as soon as per month.
How is squamous mobile most cancers diagnosed?
Your medical doctor will first operate a bodily examination and check out any strange areas for symptoms of cSCC. They’ll additionally ask you about your clinical history. If cSCC is suspected, your medical doctor may additionally determine to take a biopsy to affirm the diagnosis.
A biopsy normally entails getting rid of a very small component of the affected skin. The pores and skin pattern is then despatched to a laboratory for testing.
In some cases, your medical doctor may also want to put off a large section or all of the ordinary increase for testing. Talk with your medical doctor about any achievable scarring or biopsy concerns.
After receiving therapy for cSCC, be positive to attend all follow-up visits with your doctor. It’s feasible for the most cancers to return, so it’s fundamental to test your pores and skin for any signs and symptoms of most cancers or precancer at least as soon as per month.
Can squamous mobilephone most cancers be prevented?
To assist limit your threat of cSCC, comply with these suggestions when possible:
- Limit your solar exposure.
- Avoid the solar for the duration of the most up to date section of the day, which is between 10 a.m. and four p.m.
- Wear sunscreen that has an SPF of at least 30 on every occasion you go out in the sun.
- Wear shades with UV ray protection.
- Wear a hat and cowl your pores and skin when working outside.
- Avoid the use of tanning beds and lamps.
- Protect your pores and skin throughout wintry weather as properly due to the fact iciness UV rays can be mainly dangerous.
- Check your pores and skin every month for any new or strange growths.
- See a dermatologist as soon as per 12 months for a full-body pores and skin check.
Takeaway on Squamous Cell Cancer
Early detection of cSCC is key to profitable treatment. If cSCC isn’t handled in its early stages, the most cancers may also unfold to different areas of the body, inclusive of the lymph nodes and organs. Once this occurs, the circumstance can be lifestyles threatening.
People with weakened immune structures due to positive clinical conditions, such as HIV, AIDS, or leukemia, have a larger chance of creating greater serious types of cSCC.

Leave a Reply