Cancer Preventing Drugs: Understanding Types, Mechanisms, Benefits, and Risks
Looking for ways to prevent cancer? Cancer preventing drugs may be the answer. In this article, we’ll introduce you to these drugs and explore the different types available. You’ll also learn how they work to prevent cancer and the potential benefits and risks associated with using them. Keep reading to discover how cancer preventing drugs can help you stay healthy.
Introduction to Cancer Preventing Drugs
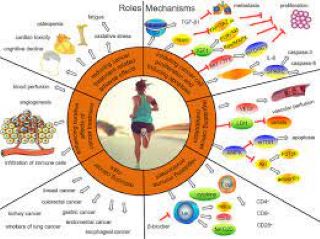
Cancer is a disease that affects millions of people worldwide. It is caused by the uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells in the body. While there are various treatments available for cancer, prevention is always better than cure. Cancer preventing drugs are medications that can help reduce the risk of developing cancer. These drugs work by interfering with the processes that lead to cancer formation, such as cell division and DNA damage. In this article, we will explore the different types of cancer preventing drugs, how they work, and their benefits and risks. By understanding these important factors, you can make informed decisions about your health and take steps to reduce your risk of developing cancer.
Types of Cancer Preventing Drugs
There are several types of drugs that can help prevent cancer. These drugs are classified based on their mechanism of action and the type of cancer they target. Some common types of cancer preventing drugs include hormone therapy, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, and chemotherapy.
- Hormone therapy drugs are used to treat cancers that are hormone-sensitive, such as breast and prostate cancer. These drugs work by blocking the production or activity of hormones that promote cancer growth. Examples of hormone therapy drugs include tamoxifen, aromatase inhibitors, and luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) agonists.
- Immunotherapy drugs help the immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells. These drugs work by targeting specific proteins on the surface of cancer cells or by boosting the immune system’s response to cancer. Examples of immunotherapy drugs include checkpoint inhibitors, CAR T-cell therapy, and cytokines.
- Targeted therapy drugs are designed to target specific molecules that are involved in cancer growth and progression. These drugs work by blocking the activity of these molecules, which can slow down or stop cancer growth. Examples of targeted therapy drugs include tyrosine kinase inhibitors, monoclonal antibodies, and proteasome inhibitors.
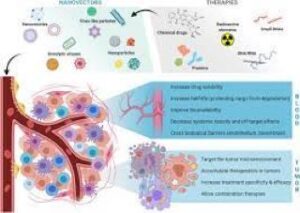
- Chemotherapy drugs are a type of cancer treatment that uses chemicals to kill cancer cells. These drugs work by interfering with the DNA or other cellular processes that cancer cells need to survive and grow. Chemotherapy drugs can be used to prevent cancer in people who have a high risk of developing the disease. Examples of chemotherapy drugs include methotrexate, cisplatin, and doxorubicin.
It is important to note that not all cancer preventing drugs are suitable for everyone. The type of drug prescribed will depend on the individual’s medical history, cancer type, and other factors. It is essential to discuss the benefits and risks of these drugs with a healthcare professional before starting any treatment.
How Cancer Preventing Drugs Work
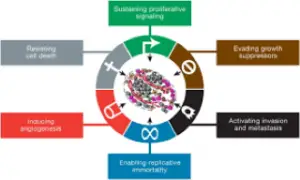
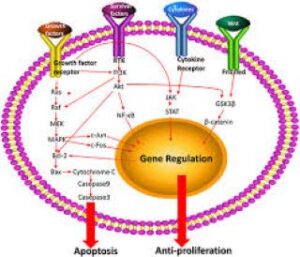
Cancer preventing drugs work by targeting specific mechanisms that are involved in the development and progression of cancer. These drugs can either prevent the formation of cancer cells or slow down the growth of existing cancer cells.
One type of cancer preventing drug is known as chemo-preventive agents, which are substances that can block the development of cancer by interfering with the DNA damage response or by inhibiting the activity of enzymes that promote tumor growth. Another type of cancer preventing drug is immunomodulatory agents, which stimulate the immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells.
Some cancer preventing drugs work by inhibiting the activity of specific proteins that are essential for cancer cell survival and proliferation. For example, targeted therapy drugs can block the activity of proteins such as epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) or vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), which are often overactive in cancer cells.
Overall, cancer preventing drugs work by targeting specific molecular pathways that are involved in cancer development and progression. While these drugs can be effective in reducing the risk of cancer, they can also have side effects and risks that need to be carefully considered before use.
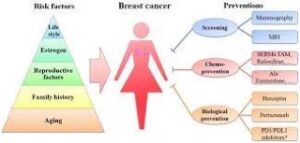
Benefits and Risks of Cancer Preventing Drugs
Benefits and Risks of Cancer Preventing Drugs:
While cancer preventing drugs can be effective in reducing the risk of developing certain types of cancer, they also come with potential benefits and risks. One of the main benefits is that these drugs can help prevent cancer from developing or spreading, which can ultimately save lives. Additionally, some cancer preventing drugs may also have other health benefits, such as reducing the risk of heart disease.
However, there are also potential risks associated with cancer preventing drugs. These drugs can have side effects, ranging from mild to severe, depending on the type of drug and the individual’s response. Some common side effects include nausea, vomiting, fatigue, and hair loss. In rare cases, more serious side effects such as blood clots or liver damage can occur.
Another potential risk of cancer preventing drugs is the cost. These drugs can be expensive, and not all insurance plans cover them. This can make it difficult for individuals who need these drugs to access them.
It’s important to weigh the potential benefits and risks of cancer preventing drugs before deciding whether to take them. Individuals should discuss their options with their healthcare provider and carefully consider their personal medical history, family history, and other factors that may impact their risk of developing cancer.

Leave a Reply